Formation of alcohols (SN2)
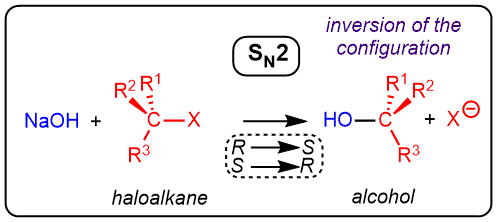
Addition of hydroxide to an alkyl halide leads to the formation of an alcohol on through an SN2 mechanism resulting in inversion of the configuration.
Mechanism

- The hydroxide anion attacks the electrophilic carbon in a SN2 manner
- This results in concomitant expulsion of the leaving group (usually a halide)
- The final product is formed with inversion of configuration.