Radical bromination of alkanes
The reaction of the bromine with the alkane in the presence of light leads to the radical bromination of the alkanes. Due to different thermodynamic stabilities, the more substituted alkyl bromide is formed.

Mechanism
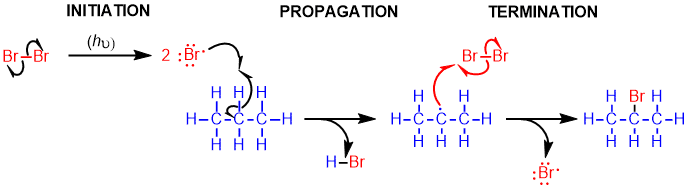
- In the presence of light, the bond of the bromine molecule is broken to form 2 bromine radicals. Since this intermediate concentration is low, it is more likely to find an alkane molecule rather than another radical intermediate (which would lead to completion of the reaction).
- Extraction of the more substituted hydrogen leads to the formation of the more substituted and, therefore, more stable radical.
- The alkyl radical reacts with a bromine molecule to form the alkyl bromide and regenerate the bromine radical.