Hydrolysis of nitriles catalyzed by acid
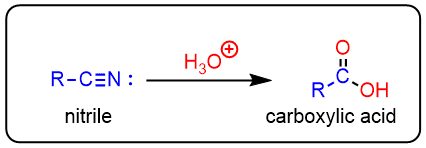
Nitriles can be hydrolyzed to carboxylic acids in acidic aqueous solutions and to carboxylated salts with base-catalyzed hydrolysis.
Mechanism
The mechanism contains two key steps:
- In the first part, the protonation of nitrogen activates the C-N triple bond for a nucleophilic attack of water.
- After deprotonation, a tautomer of an amide is formed, called imidic acid (a nitrogenous analogue of an enol and, like keto-enol tautomerization, the more stable amide tautomer prevails at equilibrium). The tautomerization mechanism can be shown in two proton transfer steps beginning with a protonation of nitrogen.
- In the second part, the amide is hydrolyzed to a carboxylic acid.
