NaBH4 reduction
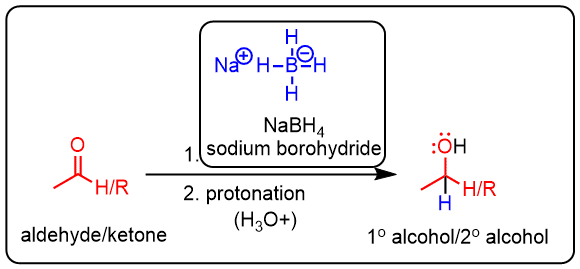
Reduction of aldehydes or ketones with sodium borohydride gives alcohols.
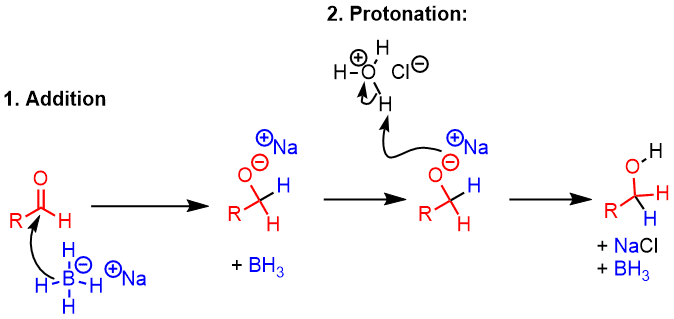
Mechanism
- In the first step, an H- breaks off from BH4- and adds to the carbonyl carbon (an example of [1,2] addition). This forms the C-H bond and breaks the C-O bond, giving rise to a new pair of electrons on oxygen, making it negatively charged.
- In the second step, a proton from water (or an acid such as NH4Cl) is added to the alkoxide to give the alcohol. This is done at the end of the reaction.