Oxidation of aldehydes to carboxylic acids with Ag2O
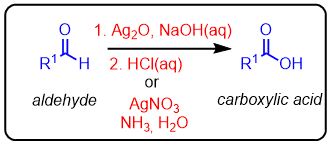
The oxidation of aldehydes to carboxylc acids can be carried out with a diaminesilver(I) complex [Ag(NH3)2]+. This reaction results in the formation of Ag metal which coats the inside of the reaction vessel. This is known as the Tollen's test and was classically used to distinguish aldehydes from ketones (which did not react under the reactions conditions).
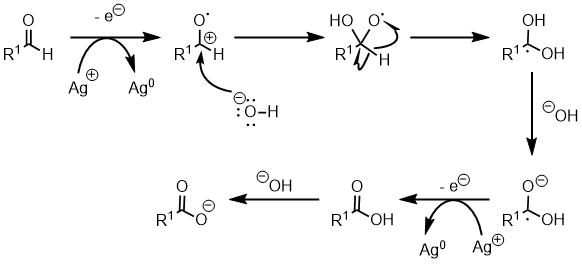
Mechanism
- The carbonyl group is oxidized in the process and the Ag +Ag+ is reduced.
- The resultant oxidized aldehyde (now a radical cation) reacts with hydroxide to form a tetrahedral intermediate. A gem-diol like intermediate is formed via a hydrogen shift, which then continues on to the final carboxylate anion.
- A gem-diol like intermediate is formed via a hydrogen shift, which then continues on to the final carboxylate anion. At the end of the reaction treatment with aqueous acid gives the carboxylic acid.