Wittig reaction
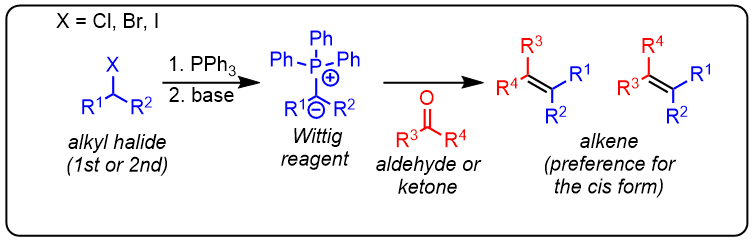
The Wittig reaction is an organic reaction used to convert a primary or secondary alkyl halide and aldehyde or ketone to an olefin using triphenylphosphine and base.
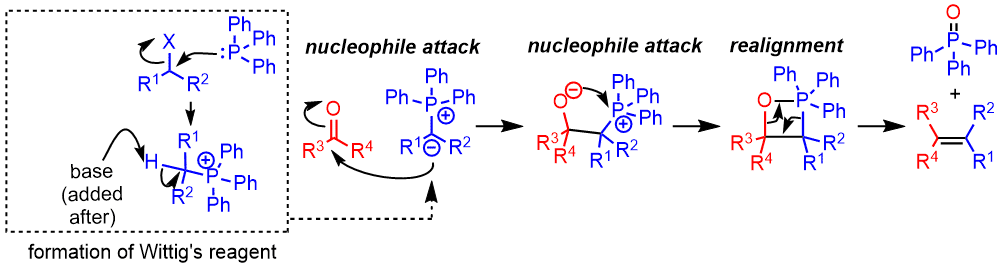
- The alkyl halide is attacked by PPh3 and releases the halogen anion and forms a phosphonium ion.
- The base is then deprotonated in the alpha position to give a phosphorus ylide. Subsequently, Wittig's reagent attacks the aldehyde or ketone.
- The oxygen anion attacks the phosphorus atom in an intramolecular attack.
- Oxophosphetane decomposes to produce an alkene and triphenylphosphine oxide. The formation of a strong P=O bond is the driving force for this reaction.